We put excellence, value and quality above all - and it shows




A Technology Partnership That Goes Beyond Code

“Arbisoft has been my most trusted technology partner for now over 15 years. Arbisoft has very unique methods of recruiting and training, and the results demonstrate that. They have great teams, great positive attitudes and great communication.”
Why Device Testing Matters: Delivering Quality Across Platforms and OS

Have you ever experienced an app crashing on your phone while it works perfectly on a desktop? That’s exactly why device testing is essential. Device testing means checking an application on multiple devices to make sure it provides a seamless user experience. In this blog, we will explore what device testing is, its different types, approaches, and strategies to ensure strong performance and smooth user experience across all devices.
Device Testing Explained
In software quality assurance (SQA), device testing is the process of testing an application on different devices, form factors, and operating systems (OS) such as iOS and Android. It checks the application’s functionality, performance, and user experience across platforms to make sure it is consistent and reliable.
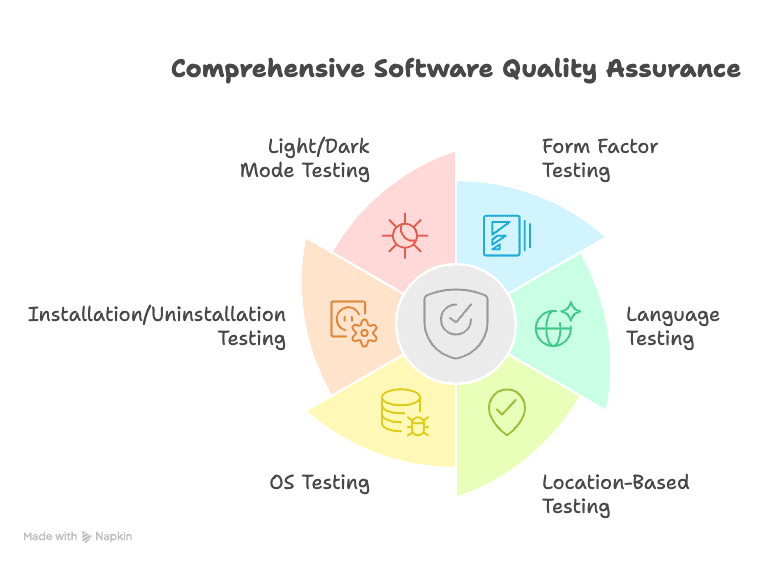
This process usually includes:
- Form factor testing
- Language testing
- Location-based testing
- OS testing
- Installation/Uninstallation testing
- Light/Dark mode testing
Importance of Different Devices
In SQA, testing on different devices is crucial because it allows applications to be checked across a wide range of devices. This reduces compatibility issues, ensures consistent functionality, and highlights environment-specific problems. It also makes sure the product works smoothly for all users, no matter which device or OS they use.
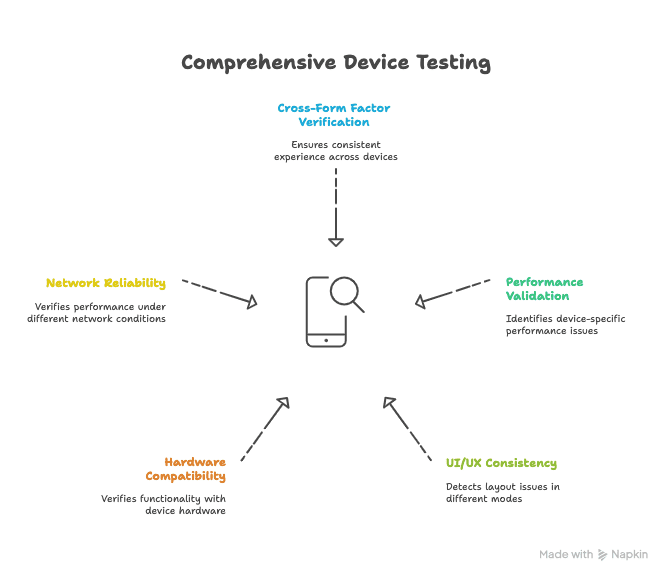
Some key reasons why testing across devices is necessary:
- Cross-form factor verification: Testing on different devices ensures a consistent experience across form factors, screen resolutions, and OS versions.
- Performance validation: Performance testing identifies issues such as memory leaks, overheating, and battery drainage that may only happen on certain devices.
- UI/UX consistency: User interface testing detects layout problems when the app is used in light or dark mode, with larger font sizes, in different languages, or when switching between portrait and landscape modes.
- Hardware compatibility: Hardware compatibility testing checks whether the application works properly with device hardware like GPS, camera, biometric authentication (fingerprint and face ID), Bluetooth, and sensors.
- Network reliability: Network reliability testing checks app performance under different conditions such as 3G, 4G, 5G, Wi-Fi, and low-bandwidth connections.
E-commerce Use Case
An e-commerce website was launched to work on desktop, mobile, and tablet devices. Testers carried out testing on different platforms and found several issues. The application was not working and was crashing on older versions of Android devices. On small screens, the UI was distorted, buttons were misaligned, and layouts were overlapping. On tablets in landscape mode, the UI appeared broken and inconsistent.
When testers ran the application on real devices, they also found problems such as battery drainage, touch issues, and network failures. All of these issues were identified and fixed through device testing. As a result, the application worked seamlessly on all platforms without problems, ensuring compatibility and usability for different users.
Types of Device Testing
Device testing can be divided into several types. Each type makes sure the application is reliable and performs well across devices and platforms.
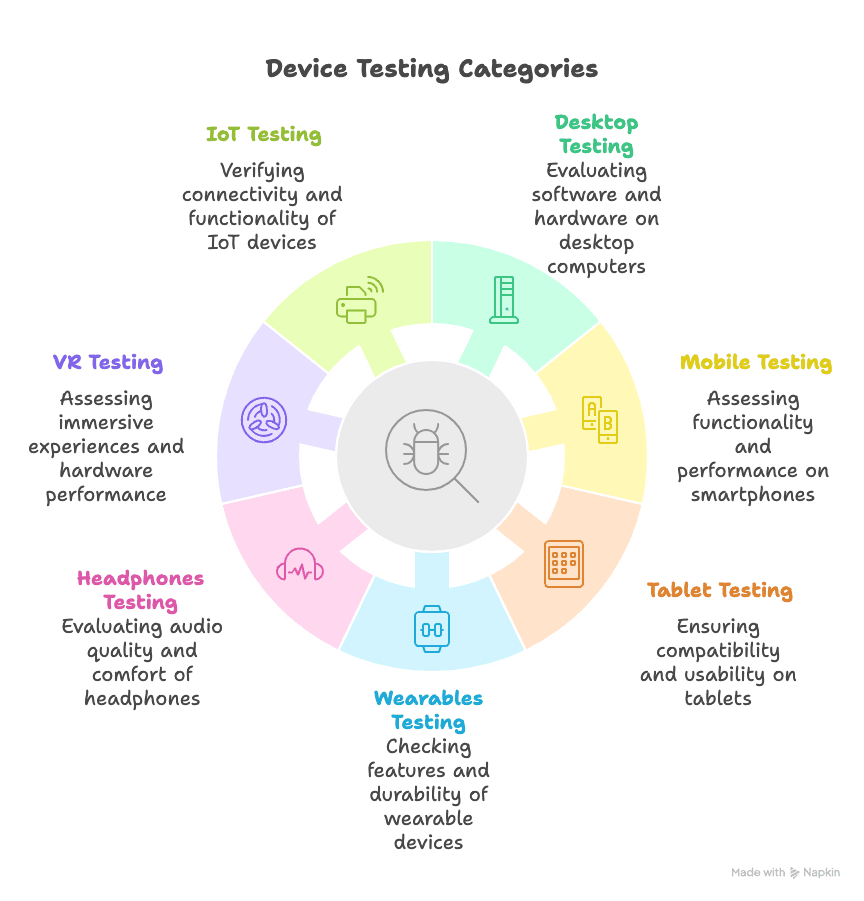
The main categories include:
- Desktop, Mobile, and Tablet testing: Verifies that applications work, respond, and display correctly across different screen sizes. This includes testing on macOS, Windows desktops, Chromebooks, iPads, tablets, and smartphones. Performing this testing ensures a smooth experience across all major form factors and OS.
- Wearables, Headphones, and VR testing: Verifies performance for devices such as smartwatches, headphones, and VR headsets. This includes checking Bluetooth and internet connectivity for wearables, audio quality for headphones, and sensor performance for VR headsets.
- IoT testing: Focuses on devices connected through the Internet of Things, such as smart home appliances, wearable devices, healthcare monitors, and security systems. It checks functionality, performance, and security.
- Real-world device testing: Runs applications on actual devices instead of emulators. This helps find issues such as high memory usage, overheating, battery consumption, and UI/UX defects.
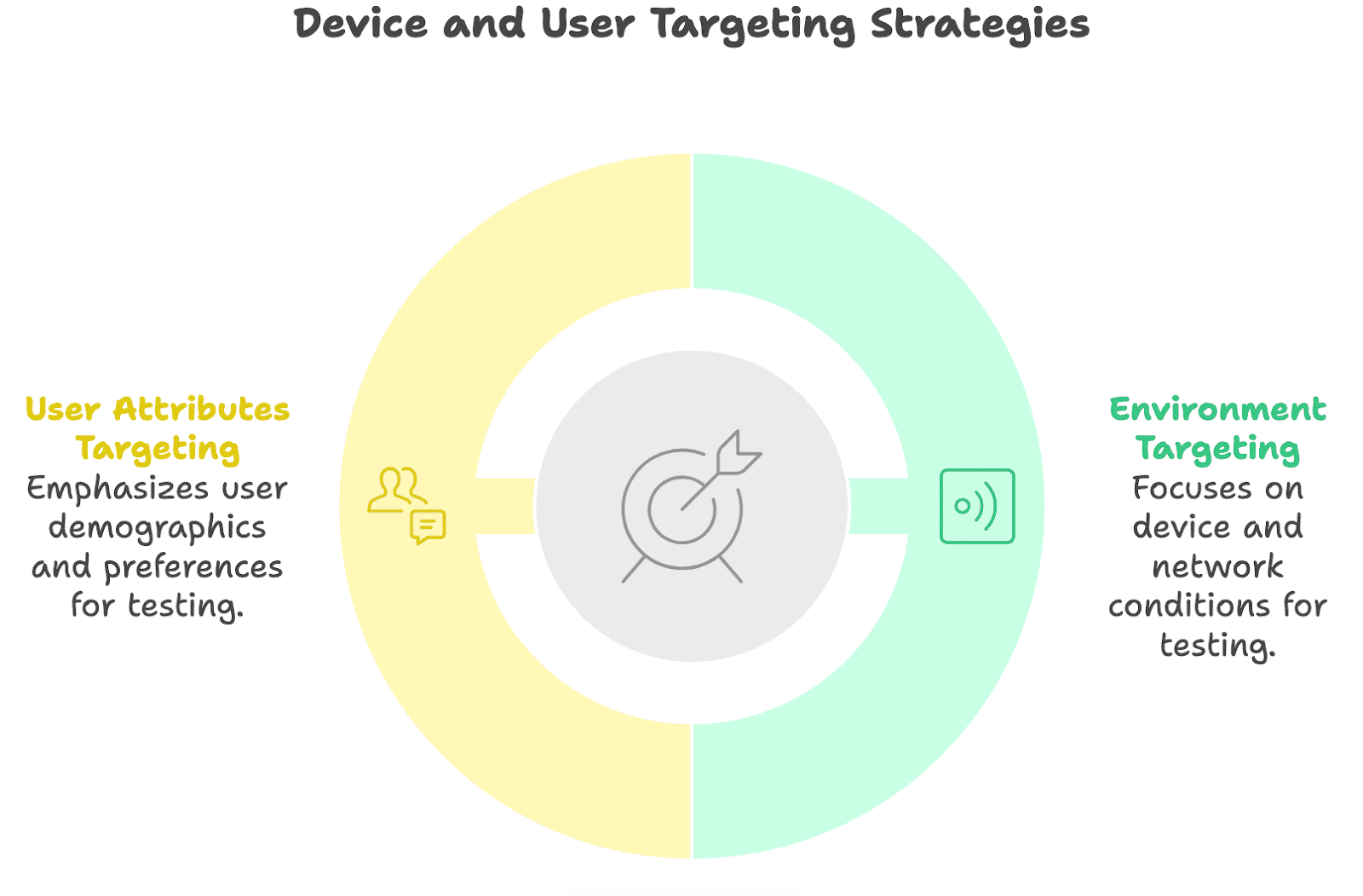
Device Targeting Coverage in Testing
Device targeting ensures applications work consistently and reliably across devices by finding issues before release. It covers both environmental factors and user attributes to deliver a smooth user experience.
Targeting by Environment
Targeting by environment makes sure the application works correctly in all the environments where users may access it, including different network conditions, locations, languages, and display modes.
Examples include:
- Testing application performance on different network conditions such as 3G, 4G, 5G, Wi-Fi, and low bandwidth.
- Checking that application features work smoothly across regions on all devices. This includes location-based services, regional restrictions, and geo-fencing.
- Verifying that the app adapts correctly to different languages based on user preferences. This includes date and time formats, currency symbols, number formats, and other regional settings.
- Ensuring the app’s theme displays correctly in both light and dark modes, supports high-contrast settings, and remains clear and readable when font size is increased.
Targeting by User Attributes
Targeting by user attributes checks real-world scenarios to see how users interact with the application. It involves end-to-end testing from the user’s perspective.
Examples include:
- Demographics testing: Checks how the application behaves for users from different age groups, locations, or genders, addressing diversity and regional needs.
- Behavioral segments testing: Ensures the application works smoothly for all user types, such as new, frequent, business, occasional, or returning users.
- User preferences testing: Verifies that user settings such as dark/light mode, language, date/time format, and notifications are applied correctly.
- Localization testing: Ensures the application is adapted for a specific region or culture, including language, locale, and date/time formats.
- Accessibility testing: Ensures the application can be used by people with disabilities. This includes testing features like keyboard navigation, screen readers, voice commands, high-contrast mode, and other accessibility tools.
In the End
In software quality assurance (SQA), device testing plays a vital role. It is one of the best ways to check the functionality and performance of an application across devices. This ensures stability, compatibility, and reliability. When users can access the same application on different devices without issues, it builds trust and satisfaction. Testing on different devices is the key to delivering a high-quality application.
























