We put excellence, value and quality above all - and it shows




A Technology Partnership That Goes Beyond Code

“Arbisoft has been my most trusted technology partner for now over 15 years. Arbisoft has very unique methods of recruiting and training, and the results demonstrate that. They have great teams, great positive attitudes and great communication.”
From Manual to Intelligent: A QA Engineer's Roadmap to AI-Powered Test Automation
In today’s fast-moving software development world, quality assurance (QA) is no longer just a task at the end of the cycle. It has become a creative and proactive part of the entire development process. While manual testing still plays a key role—especially for exploratory and user-centered testing—it can’t keep up with the fast pace of Agile and DevOps models.
Test automation helps solve speed and scalability challenges, but even it has limitations. With growing system complexity and shorter release times, QA engineers must now be more creative, adaptive, and AI-driven to stay efficient. This blog offers a step-by-step guide for testers to go from manual testing to intelligent automation using tools like Cypress, Postman, and AI-powered platforms such as Testim and Applitools.
Why Manual Testing Isn’t Enough
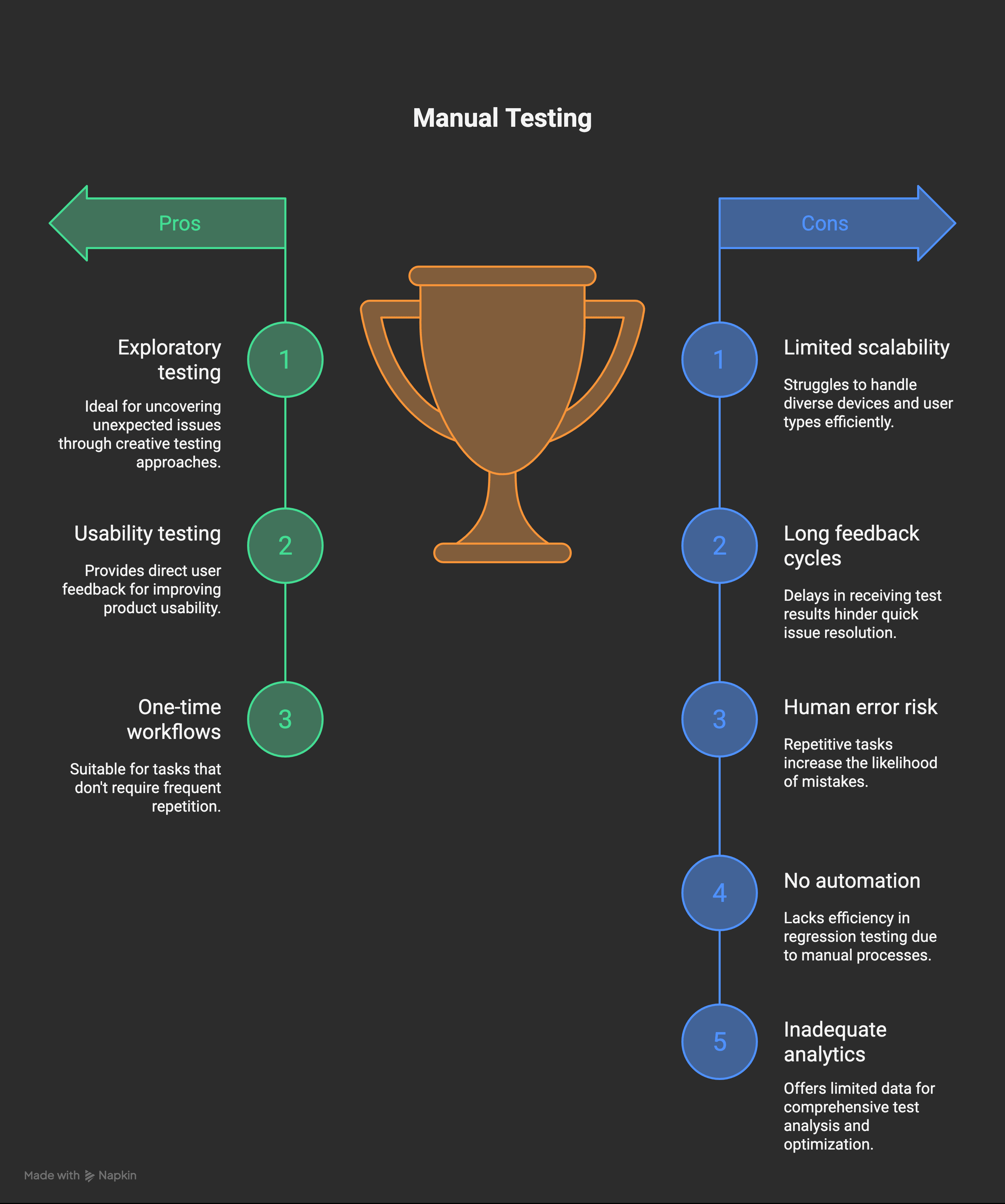
Manual testing is great for tasks like exploratory testing, usability evaluation, and one-time workflows. But in fast-changing environments that need continuous testing, manual efforts fall short. That’s why teams are turning to AI-powered automation.
Here’s why companies are moving away from relying only on manual testing:
- Limited Scalability: Manual testing can’t efficiently cover multiple devices, platforms, or user scenarios.
- Slow Feedback Loops: Developers wait longer for results, which delays bug fixing.
- Risk of Human Error: Repeating the same tests increases the chances of mistakes.
- No Automation: Regression testing takes more time and is more error-prone.
- Lack of Analytics: Manual testing doesn’t offer detailed insights into test coverage or failure patterns.
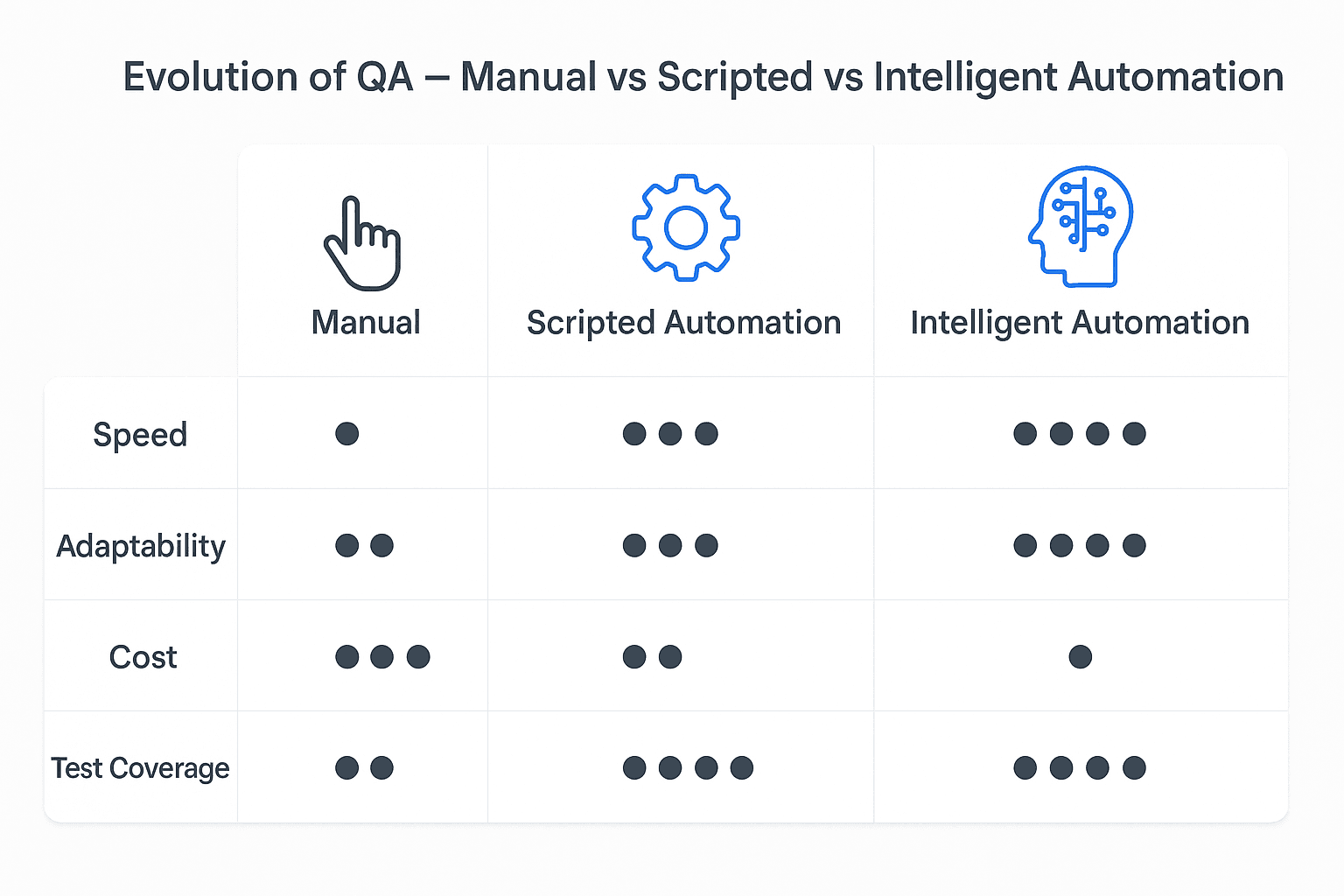
Figure 1: Manual, Scripted, and Intelligent Automation compared across speed, adaptability, cost, and test coverage.
This is where the idea of ‘Intelligent Automation’ comes in, which we’ll explain later in this blog.
Step 1: Start with Scripted Automation
Automated testing helps testers write scripts that repeat and validate actions automatically. This frees manual testers to focus on more meaningful tasks while speeding up feedback loops.
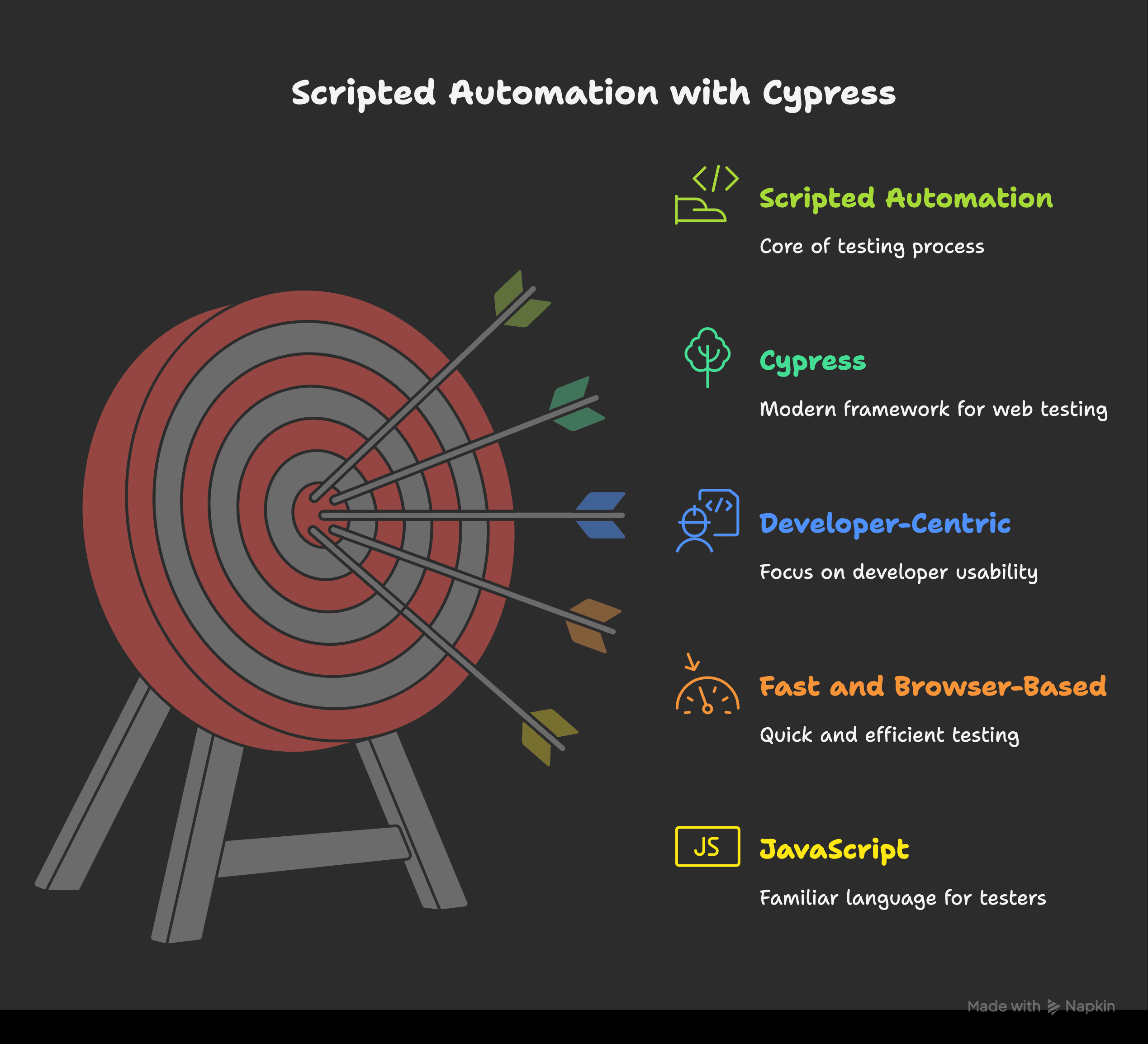
Why Cypress?
Cypress is a modern tool built for end-to-end (E2E) testing in web applications. It’s fast, browser-based, and uses JavaScript—making it familiar for many testers.
Key Cypress features:
- Built-in waiting, retries, and assertions
- Screenshots and video recording
- Easy debugging with an interactive test runner
- Strong community and excellent documentation
Example: Cypress Login Test
describe('Login Test', () => {
it('logs in successfully', () => {
cy.visit('https://app.example.com/login');
cy.get('[data-testid="email"]').type('test@example.com');
cy.get('[data-testid="password"]').type('securePass123');
cy.get('[data-testid="submit"]').click();
cy.url().should('include', '/dashboard');
cy.contains('Welcome').should('be.visible');
});
});
Tools to Integrate Early
- Postman: For testing APIs, token authentication, and request chains
- TestRail: Organize test cases and link them to JIRA tickets
- GitHub Actions: Automatically run tests as part of CI/CD
- Jenkins or CircleCI: Manage test pipelines efficiently
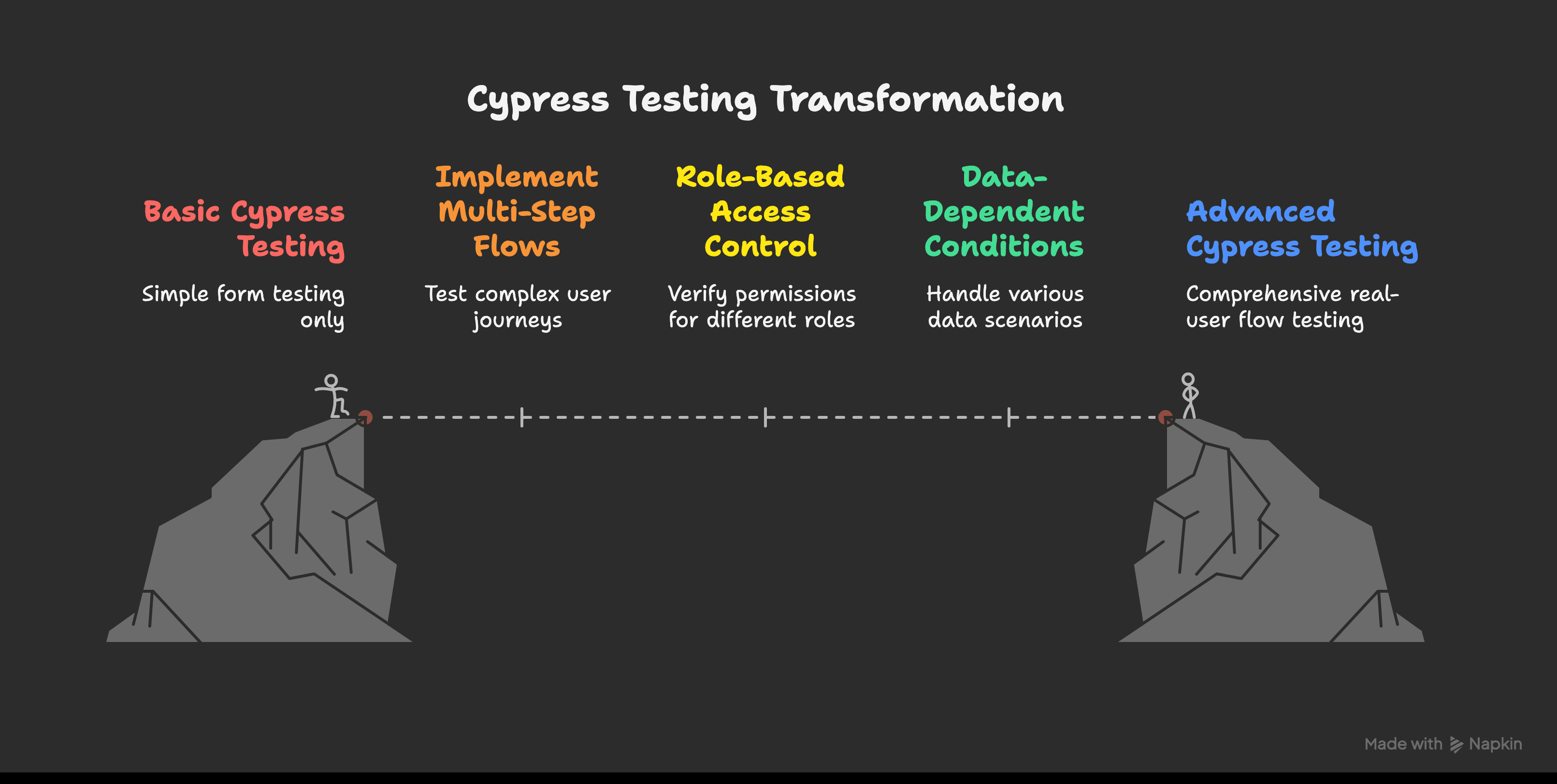
Cypress to Real User Flows
Basic login tests are just the start. Real-world apps include multi-step flows, role-based access, and data-driven behavior. Expand your testing scope to cover these.
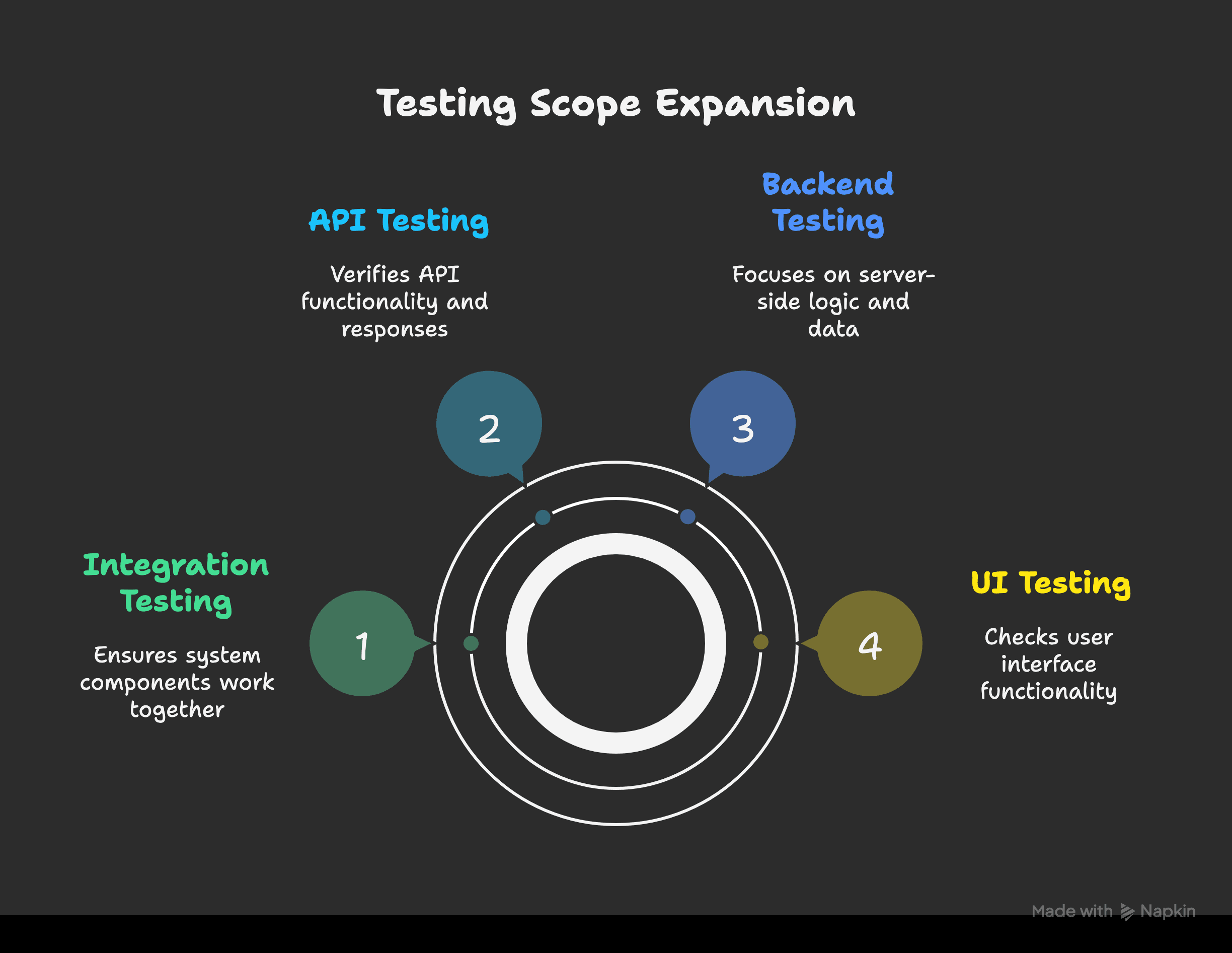
Expand Testing: UI and Backend
UI testing is essential, but backend testing is equally important. Tools like Postman or REST Assured can help validate APIs, simulate errors, and support integration testing.
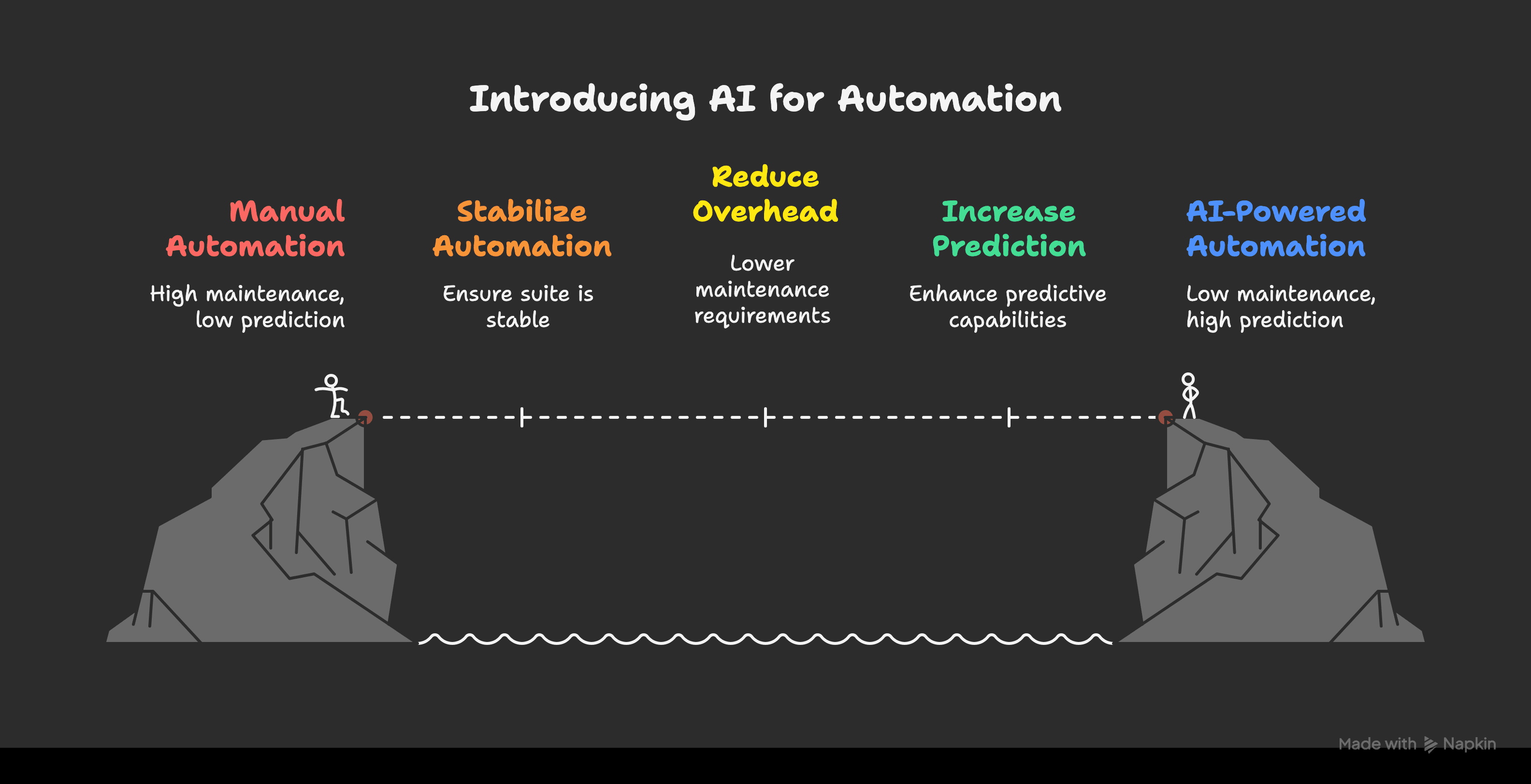
When and Why to Add AI
Once your test automation suite is stable, it’s time to add AI to lower maintenance and increase predictive accuracy.
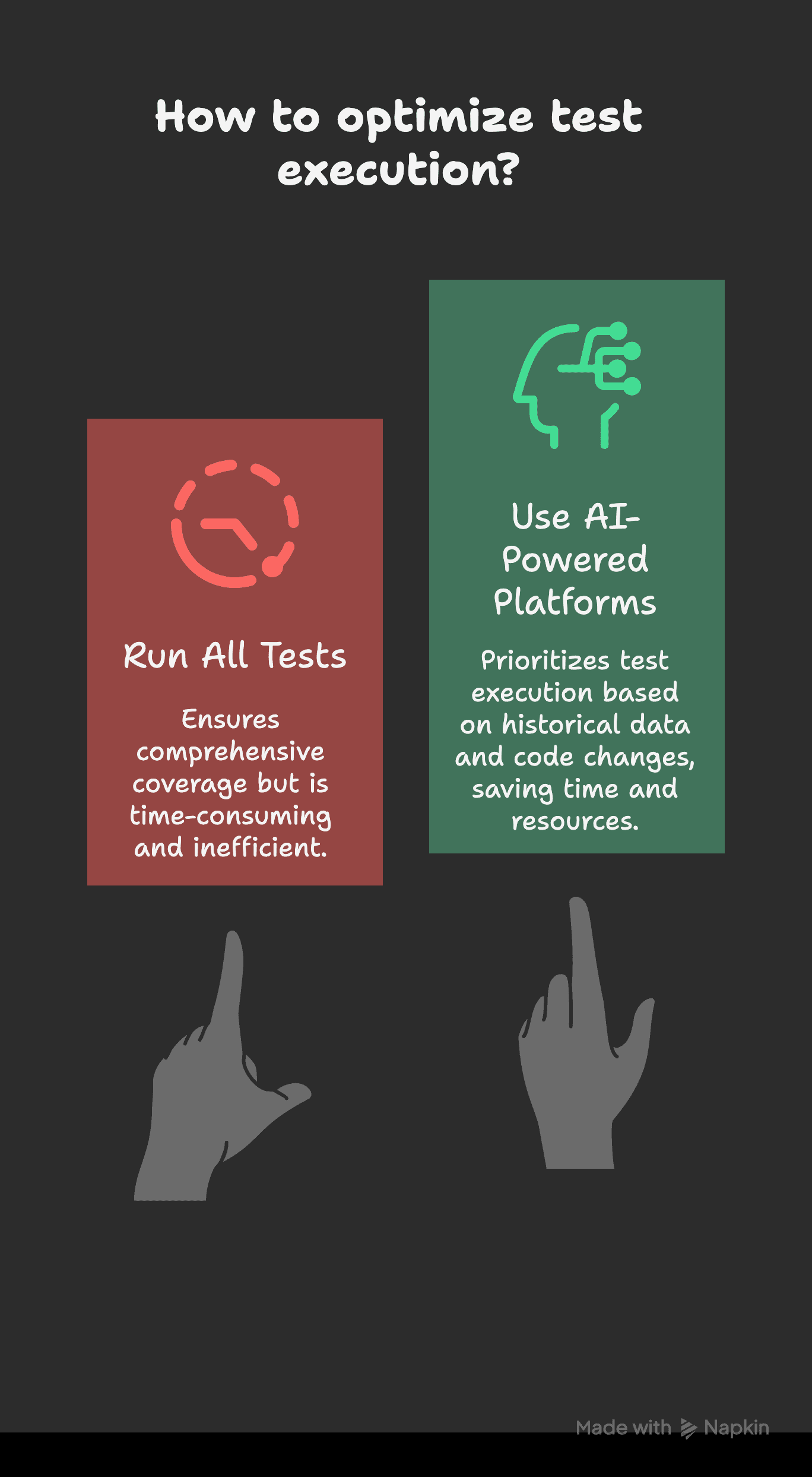
Smart Test Selection with AI
Running every test on every commit wastes time. AI-powered platforms like Launchable and TestBrain help select which tests to run based on past test data and current code changes.
Bonus: Add Security and Accessibility Testing
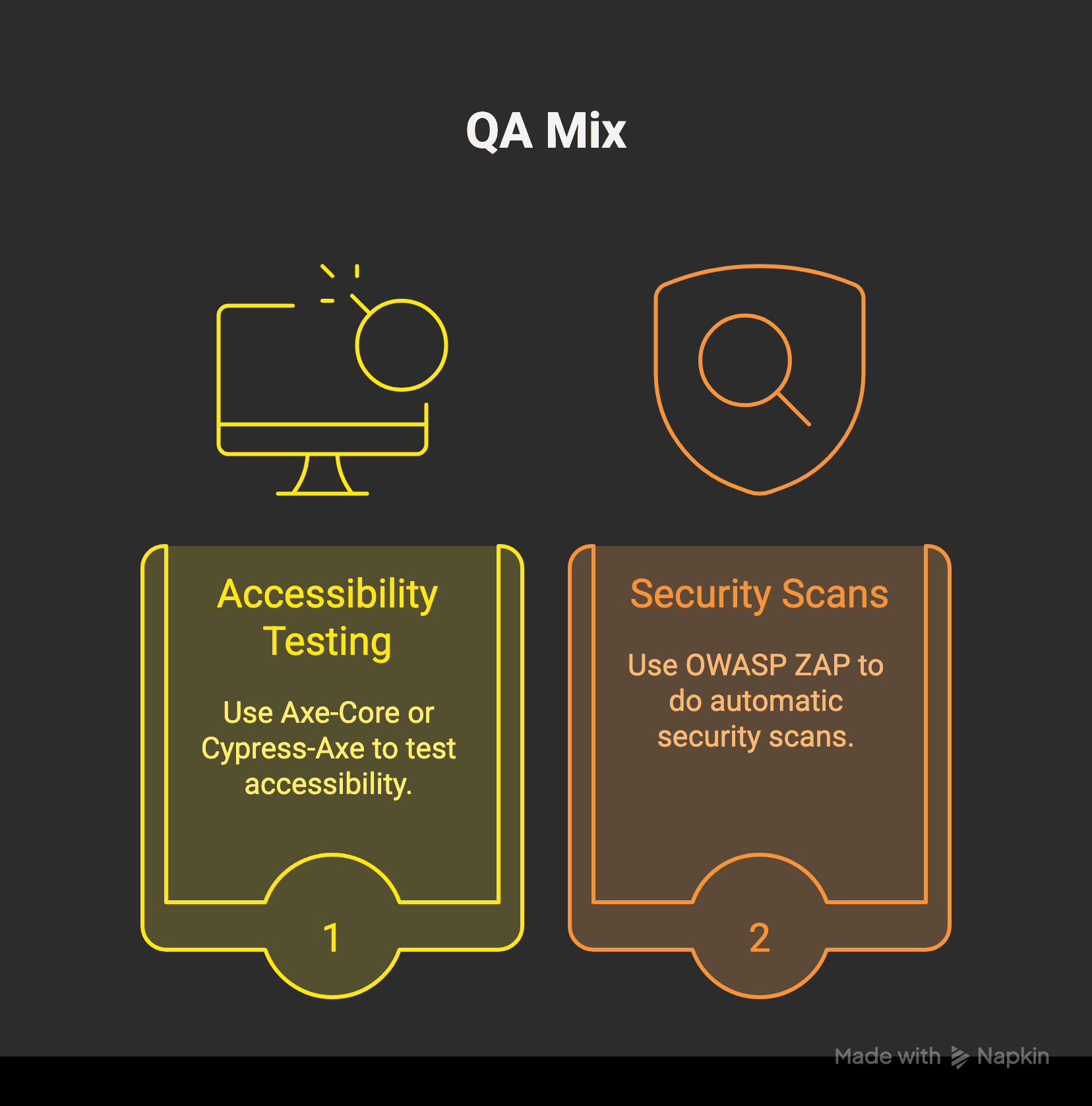
Modern QA should also focus on accessibility and security.
Accessibility Tools: Use axe-core or Cypress-Axe for accessibility testing.
Security Tools: Use OWASP ZAP to scan for security risks.
Last Tip: QA Career Development with AI
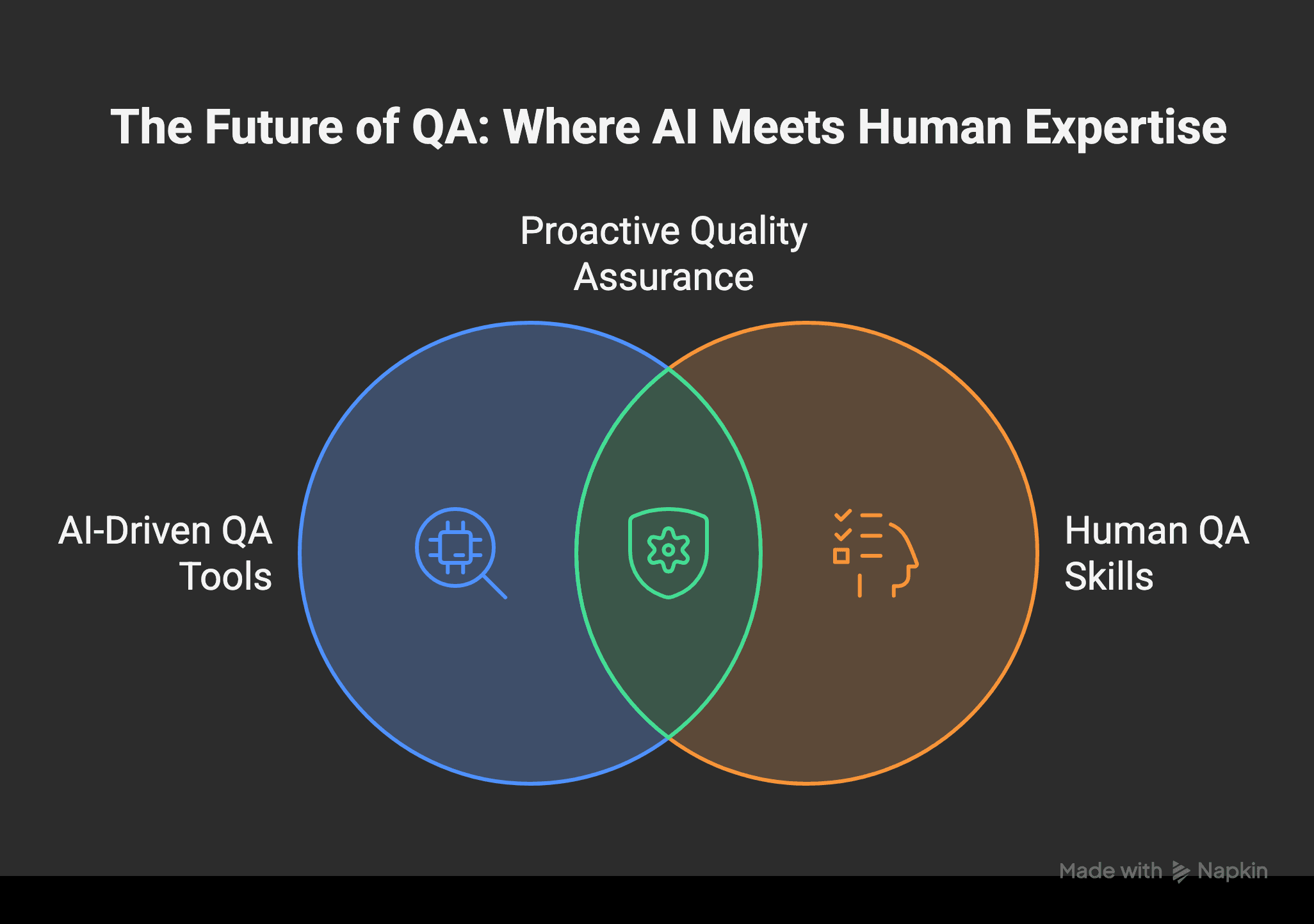
QA isn’t just about finding bugs anymore – it’s about predicting problems, preventing them from happening, and ensuring quality stays high even when projects get big.
In the future, working with AI tools and interpreting data will be key for QA careers. These skills will allow you to play a more critical role in ensuring products are high-quality. While AI is becoming more common in QA, you need to learn and adapt to stay ahead and prepare for what’s next.
Step 2: Add Intelligence with AI-Powered Automation
Once you’ve built a strong base of test automation, adding AI makes everything run more smoothly and efficiently. These tools use machine learning to reduce repetitive work, improve performance, and catch bugs more accurately.
Using AI in QA leads to smarter, faster, and more reliable processes. It fits naturally into the QA workflow and opens doors to even better testing practices, as shown in Avalonia UI’s headless testing guide.
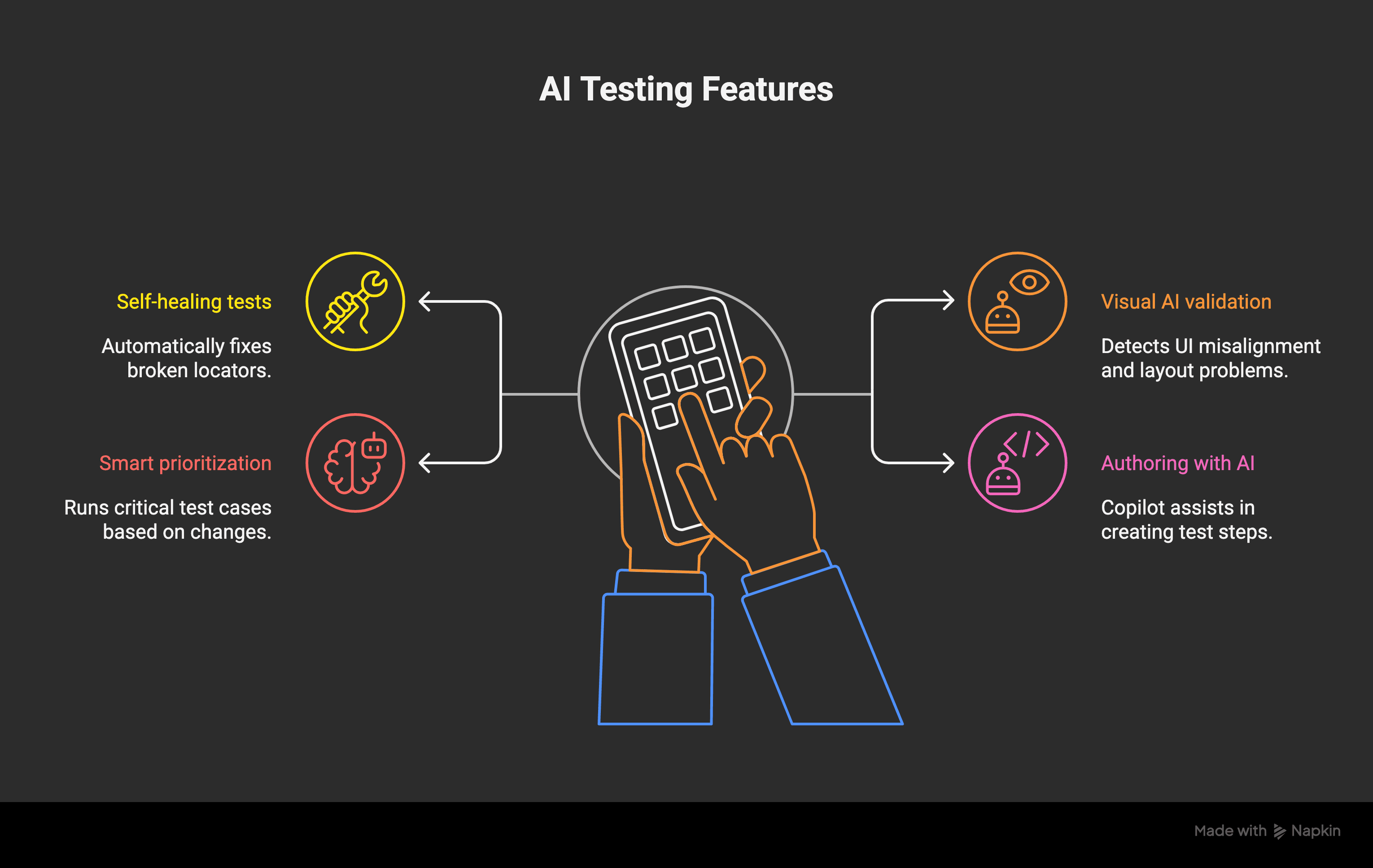
What Makes Test Automation ‘Intelligent’?
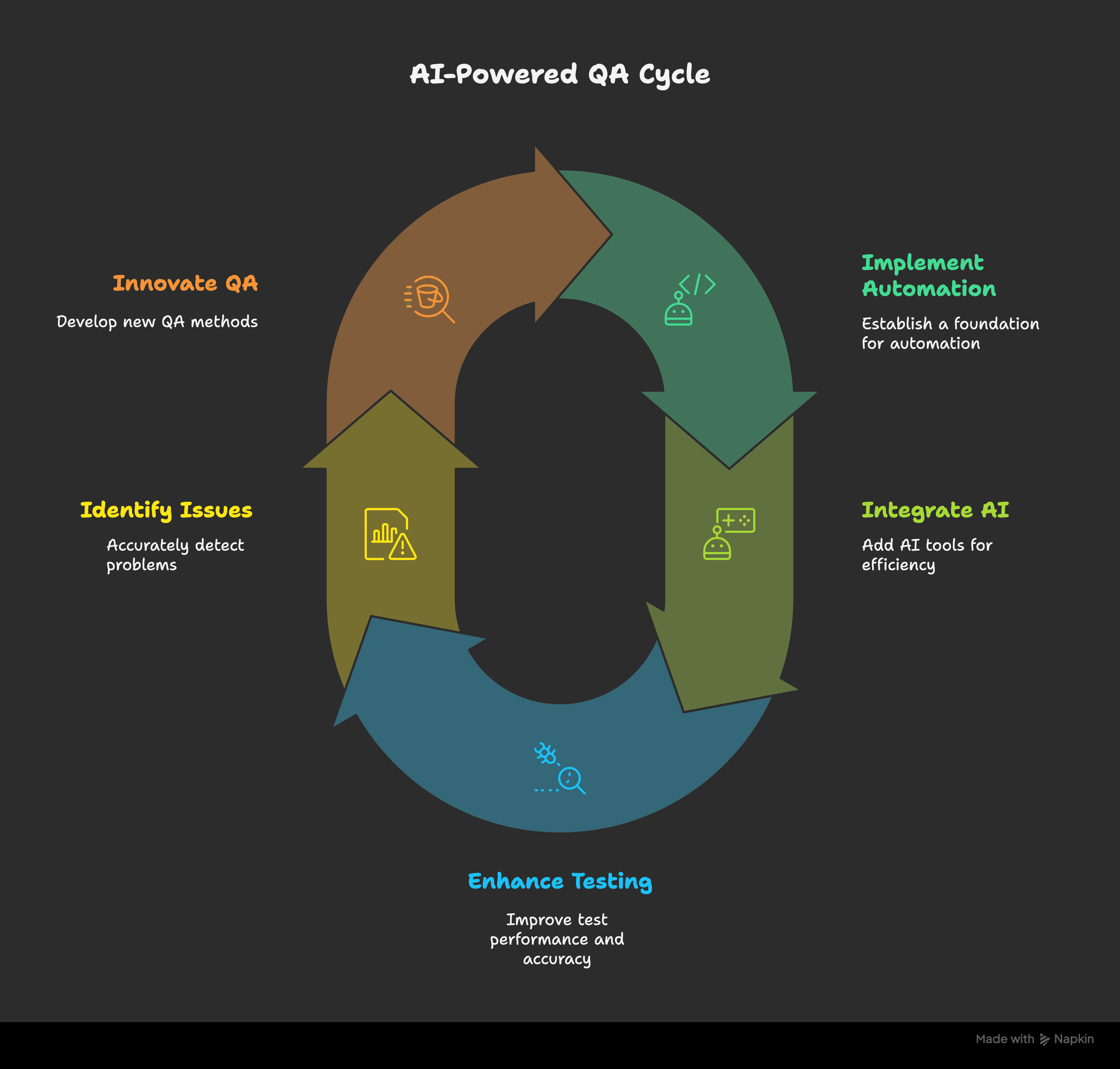
- Self-healing tests: Fix broken locators automatically
(Tools: Testim, Functionize) - Visual AI validation: Detects layout problems, color mismatches, and visual bugs
(Tool: Applitools) - Smart prioritization: Focuses only on tests likely to break
(Tool: Mabl) - AI-assisted authoring: Copilot auto-suggests test steps while you write
Self-Healing Test Logic Example
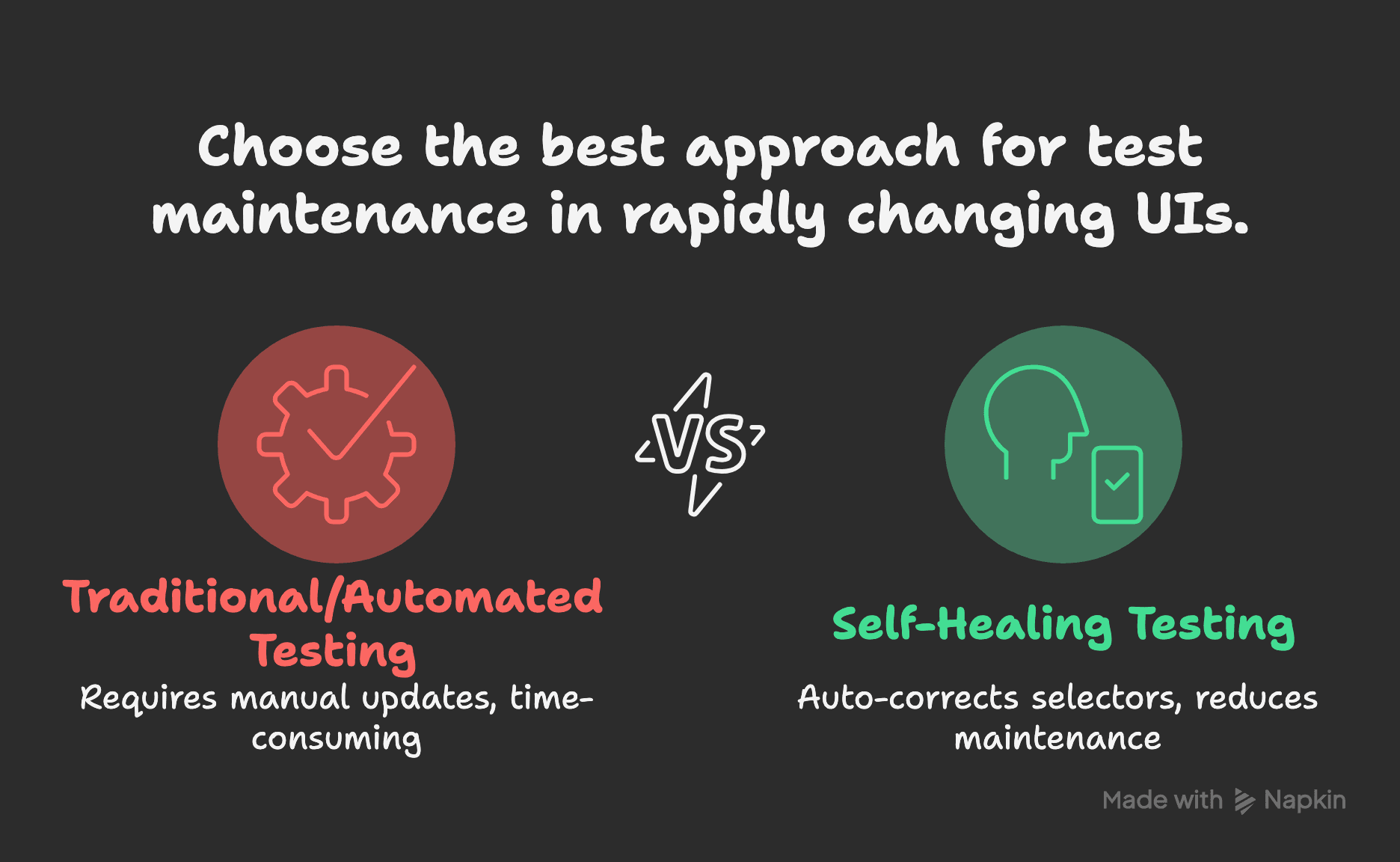
Let’s say you change a button’s CSS class in the UI. This update breaks 25 test cases. In traditional automation, you’d fix each test manually. But tools like Testim or Functionize detect that the button’s text “Submit” is still the same and update the locator automatically. This reduces over 60% of routine maintenance, especially useful in fast-changing UIs or A/B tests.
Cypress + GitHub Copilot Integration
When writing Cypress tests, GitHub Copilot speeds up the process by suggesting relevant code based on what you're typing. It’s especially useful for beginners writing JavaScript-based QA tests.
AI in Visual and Accessibility Testing
If you're already using Applitools for visual testing, you can now add tools like axe-core AI or Microsoft Accessibility Insights. These detect hard-to-spot issues like contrast errors or improper ARIA usage. They even recommend WCAG-compliant fixes and can be added to your CI/CD pipeline to fail builds if critical issues are found. This improves both quality and inclusiveness, which is now a must-have for many teams.
Best Practices for a Smooth Transition
Use data-testid attributes to make elements easy to find
Start with important flows like login, signup, and CRUD
Keep test cases small and modular
Use fixtures/config files for test data
Regularly fix or remove flaky tests
AI-Driven Analytics and Dashboarding
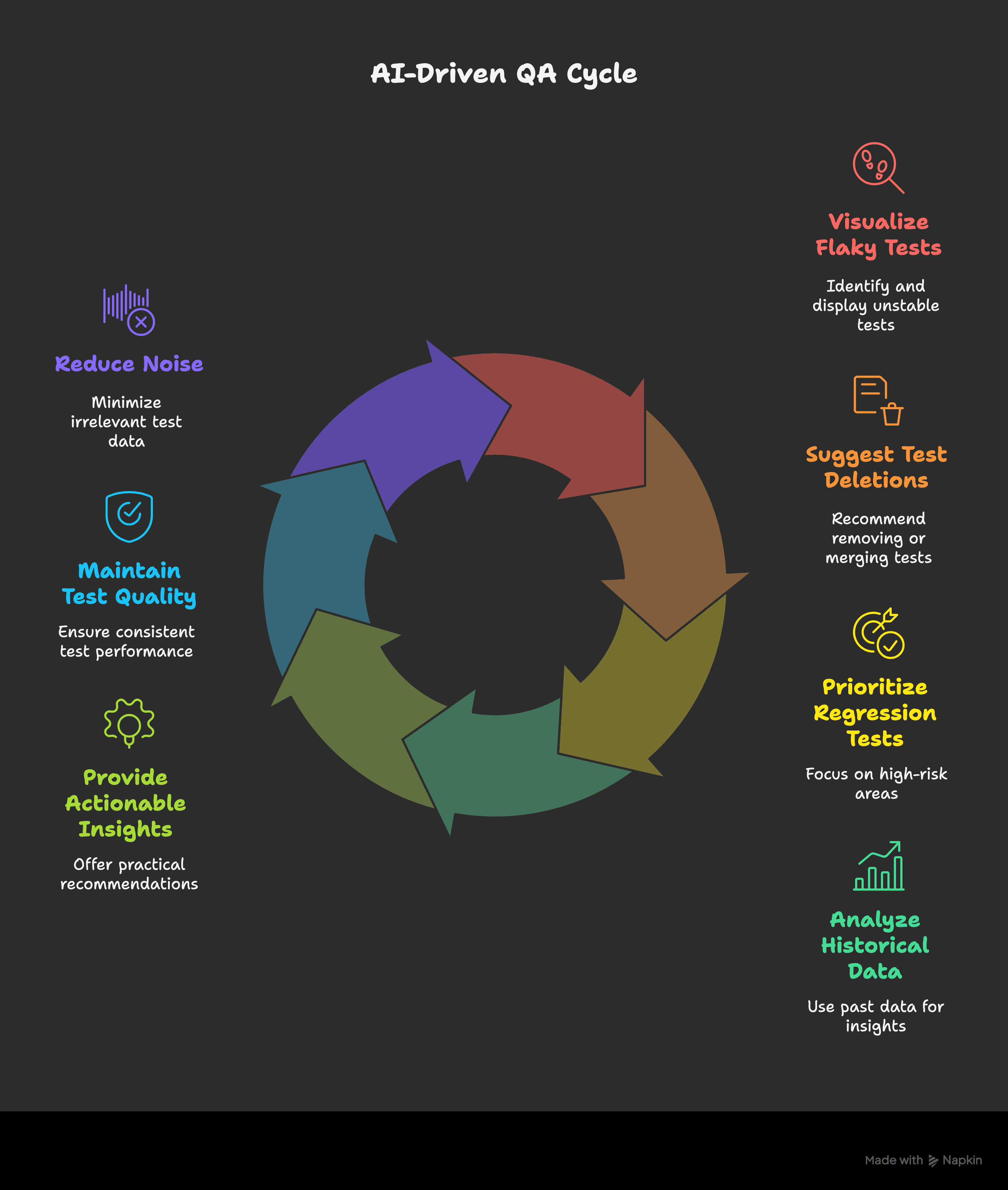
As your automation grows, it becomes harder to track everything manually. That’s where AI dashboards help.
Tools like Allure TestOps, Testim, and Launchable now provide dashboards that:
Highlight flaky tests across branches
Recommend deleting or merging unused test cases
Prioritize tests based on high-risk code commits
These dashboards use past test data to offer actionable insights, so you can improve QA without the noise.
Conclusion
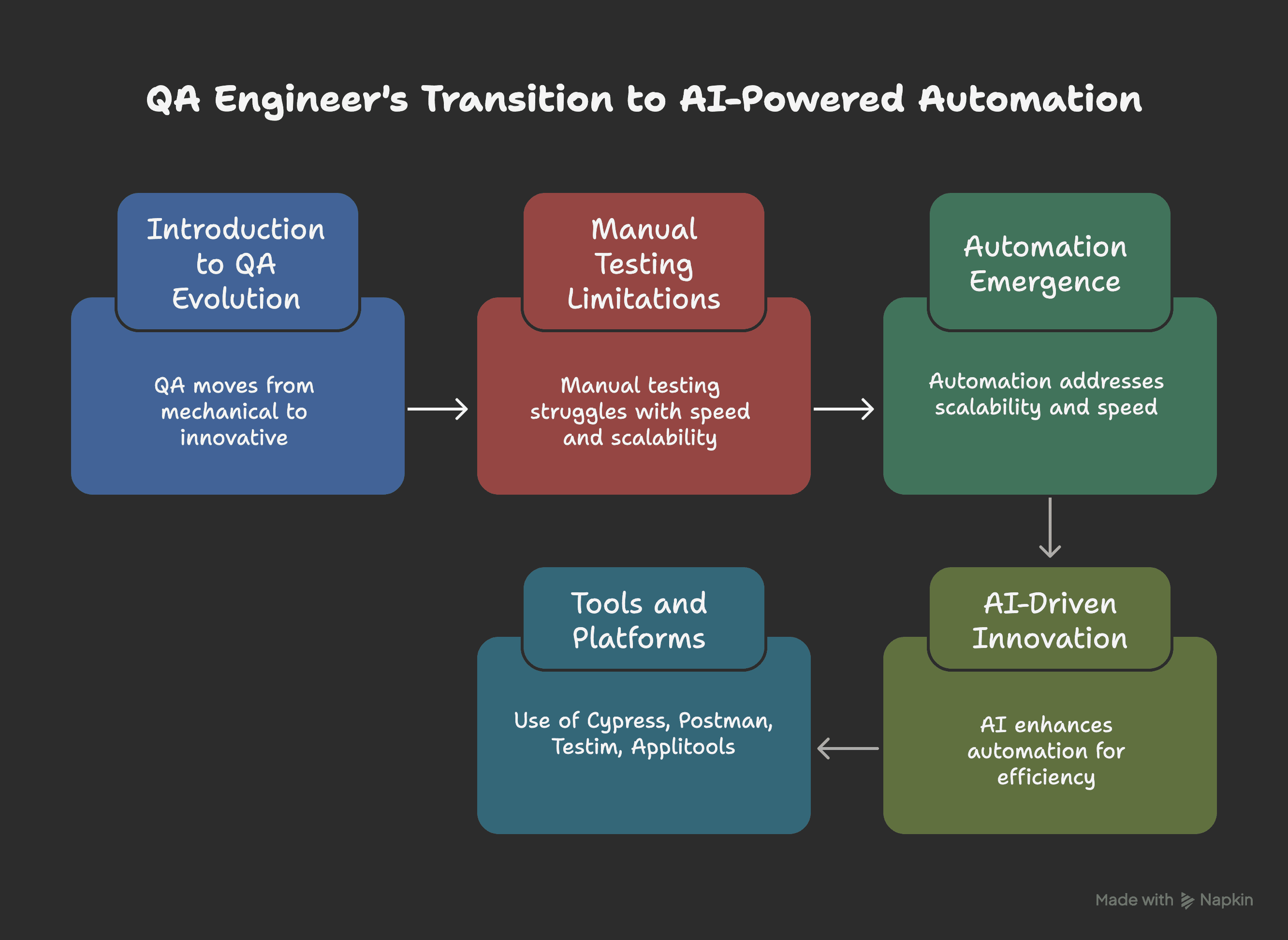
Switching from manual QA to intelligent automation isn’t a single step—it’s a journey. First, build confidence with basic automation practices using tools like Cypress and Postman. Then, gradually bring in AI platforms for smarter, faster, and more scalable QA.
By using both automation and AI, QA engineers can become key players in the software development lifecycle. With tools like Applitools, Testim, and GitHub Copilot, you’re not just running tests—you’re leading quality.
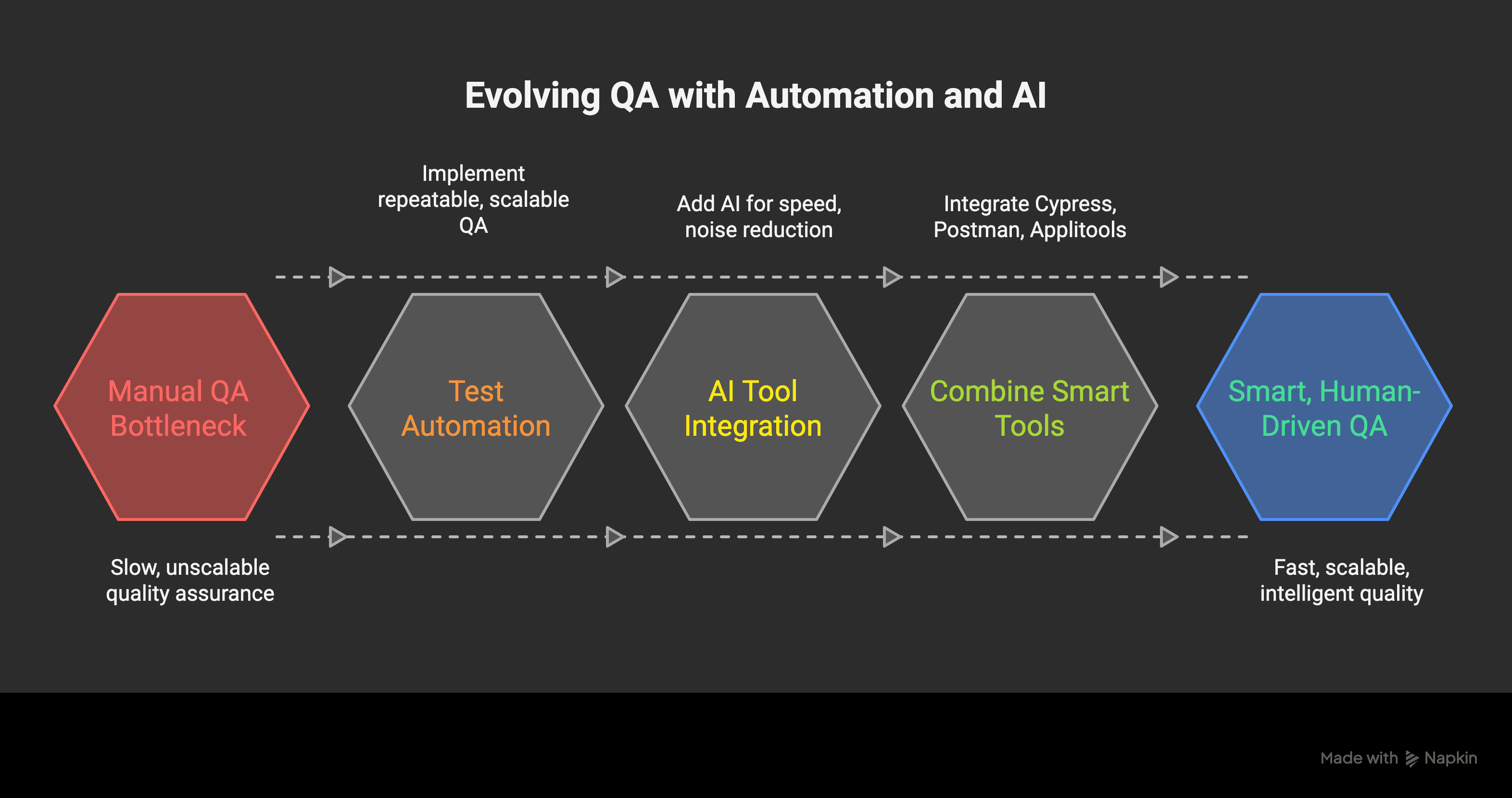
QA today isn’t just about automation. It’s smart, learning, and still deeply human.
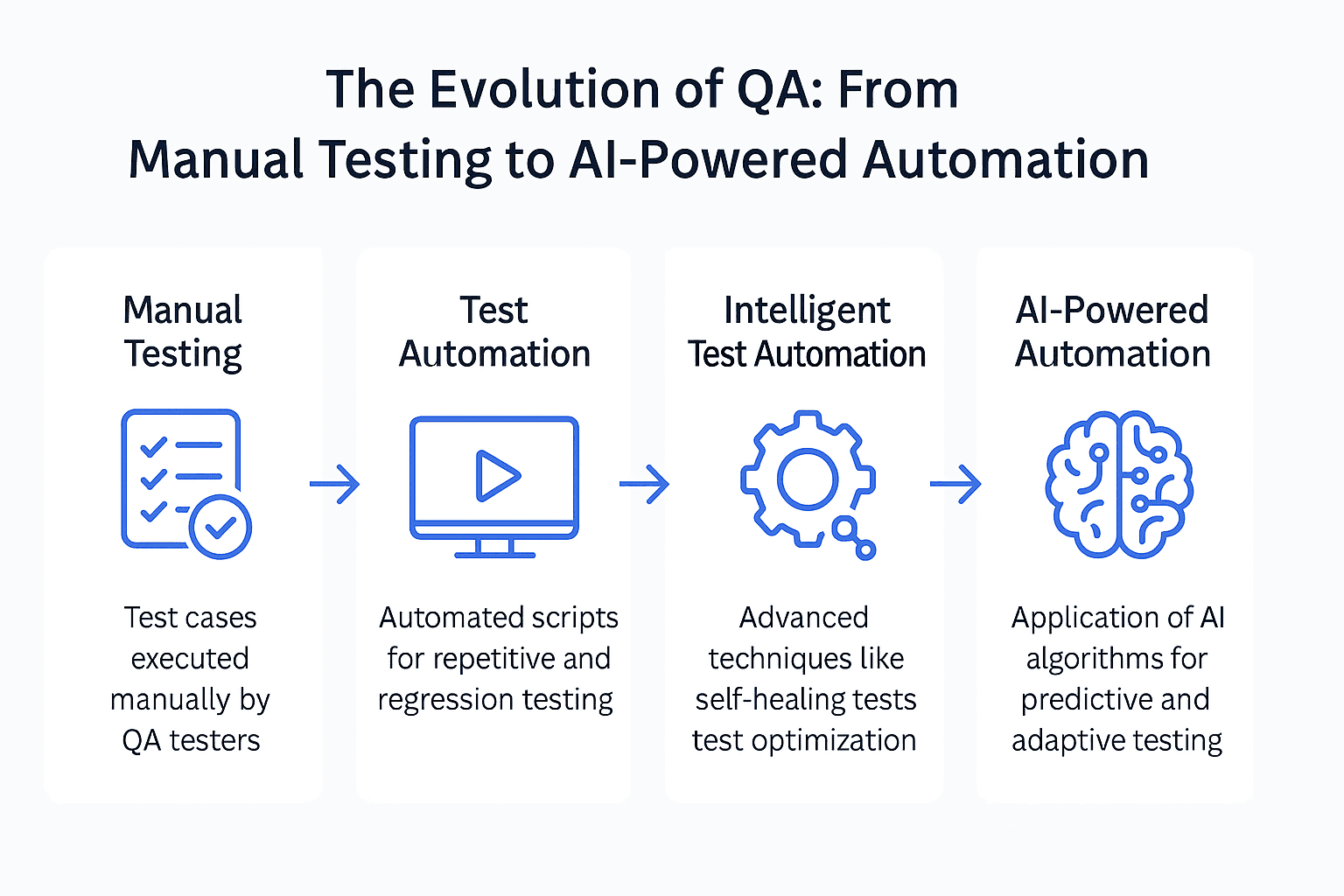
Figure 2: The journey from manual testing to AI-powered automation.
























